Scope
Humans are able to distinguish the counterparts of an object even when there are differences in illuminations and presence of shadows in the scene. Differences in illumination cause measurements of object colors to be biased toward the color of the light source. Shadows make it difficult for state-of-art algorithms to implement an efficient segmentation. However, Humans have the ability to solve these two separate problems. They are able to distinguish between reflectance and shadowing information and they implement color constancy: They perceive the same color of an object despite large differences in illumination. Segmentation is a very important prior step to implement before object recognition or categorization and color provides powerful information in these tasks, however, colorbased camera-obtained images are sensitive to many factors, such us changes in the illumination, changes in the viewing directions, etc.
State-of-art segmentation techniques apply the segmentation to the image under analysis and have to face problems due to changes in illuminants, shadowing and shadows, etc. Few works have been reported applying segmentation to the reflectance images, which are free of all the problems that illumination involves.
To implement efficient segmentation a three-stages strategy using reflectance images has been implemented. First, a color constancy algorithm is applied to the images. Secondly, intrinsic images (Reflectance and Shadowing) images are obtained using invariant ratios and a color-retinex based algorithm. Finally, a segmentation algorithm based on Kmeans and Graph-Cuts is applied to the reflectance image. A groundtruth database is used to measure the accuracy and improvement of our algorithm.
Collaborations
Intelligent Systems Lab Amsterdam ISLA, University of Amsterdam
Images
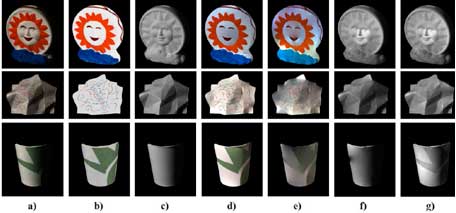

Fig. 2. Segmentation results obtained using the original images and the reflectance images. Column a) corresponds to the original images. Column b) shows the regions segmented using the original images. Column d) shows the segmentation obtained using the reflectance images appearing in column c).
Publications
- Conference ProceedingsJ.A. Pérez-Carrasco, A. Sáez, C. Serrano, B. Acha, T. Gevers, “Reflectance-based Segmentation using photometric and illumination invariants”, submitted to 2012 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Orlando, Florida, U. S. A. 2012.




