In the following we briefly outline how the software works. For further information, you may find a full document with the Aracne user’s manual here.
We also provide a test image to begin with, that you may download to test the software.
Once Aracne is running:
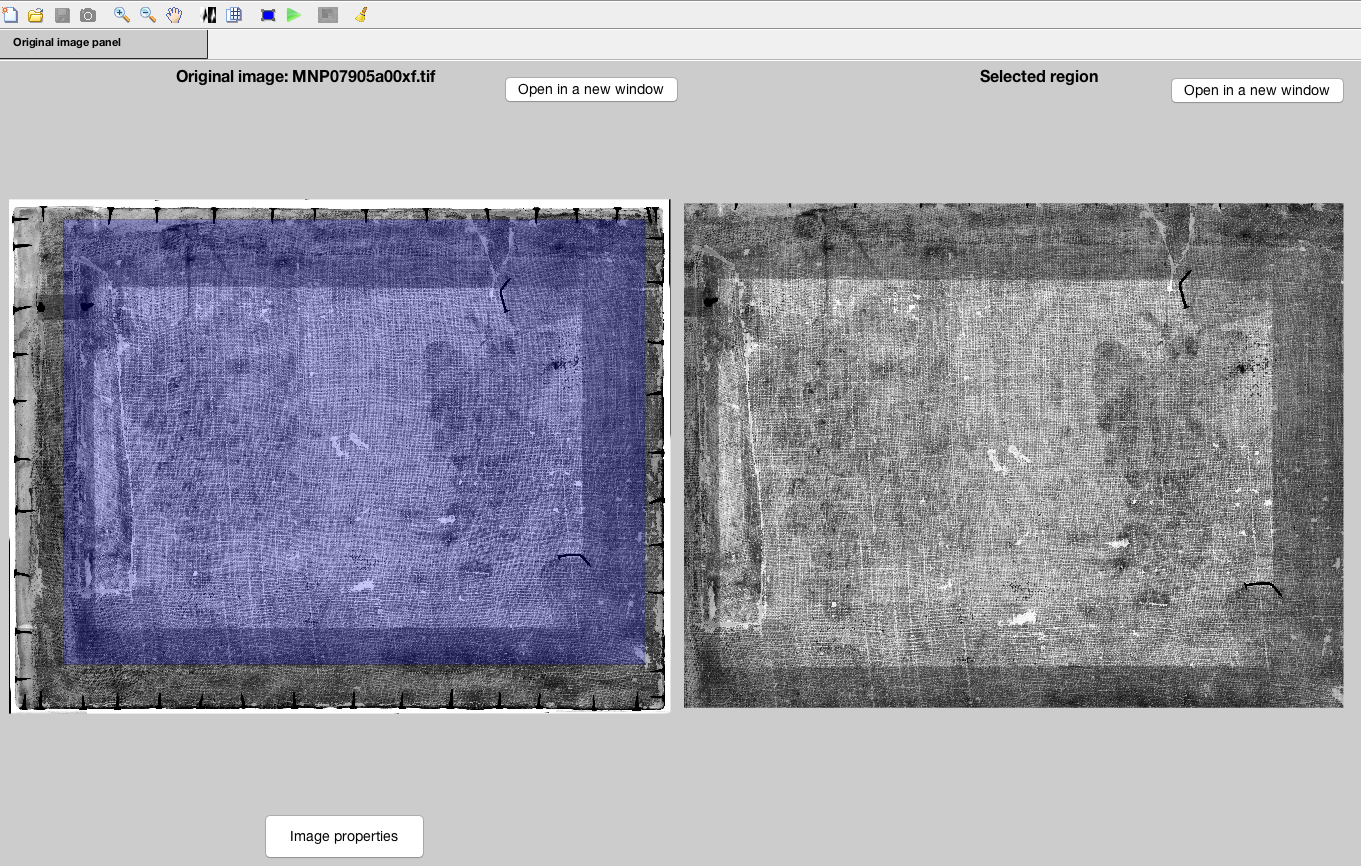
- Upload an image either using the icons in the toolbar or going over the menu windows. Once one is selected, it will appear on the left side of the screen.
- The area selection tool will become available, thus, it must be clicked on and a window showing the instructions of how to select a region will pop up, please proceed as indicated. Dragging the mouse will generate a rectangle, and double clicking on it will make the selection effective. The corresponding region will be shown in the rightmost part.
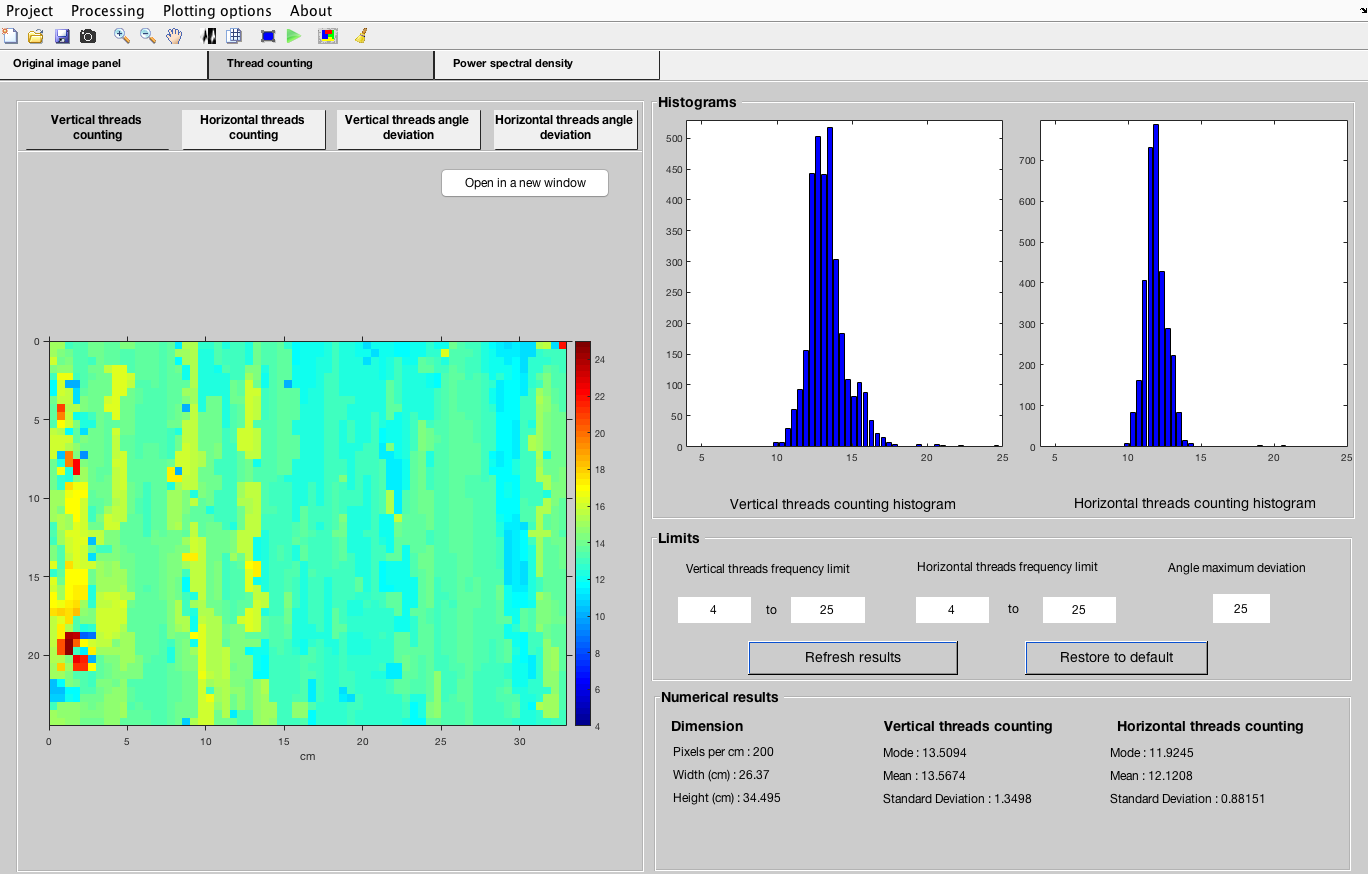
Now the thread counting process can begin. Click ‘Start processing’ in the toolbar or ‘Processing > Begin’ from the menu windows and the algorithm will start. Wait until it is finished and a results window appears on screen.- Two results tabs have become available. ‘Thread counting’ contains the results of the thread counting and angle deviation (both vertical and horizontal) in four sub tabs, two frequency histograms, and some boxes with which the user can modify the appearance of the results by altering the frequency limits and the maximum angle deviation (the algorithm will not be affected by these).
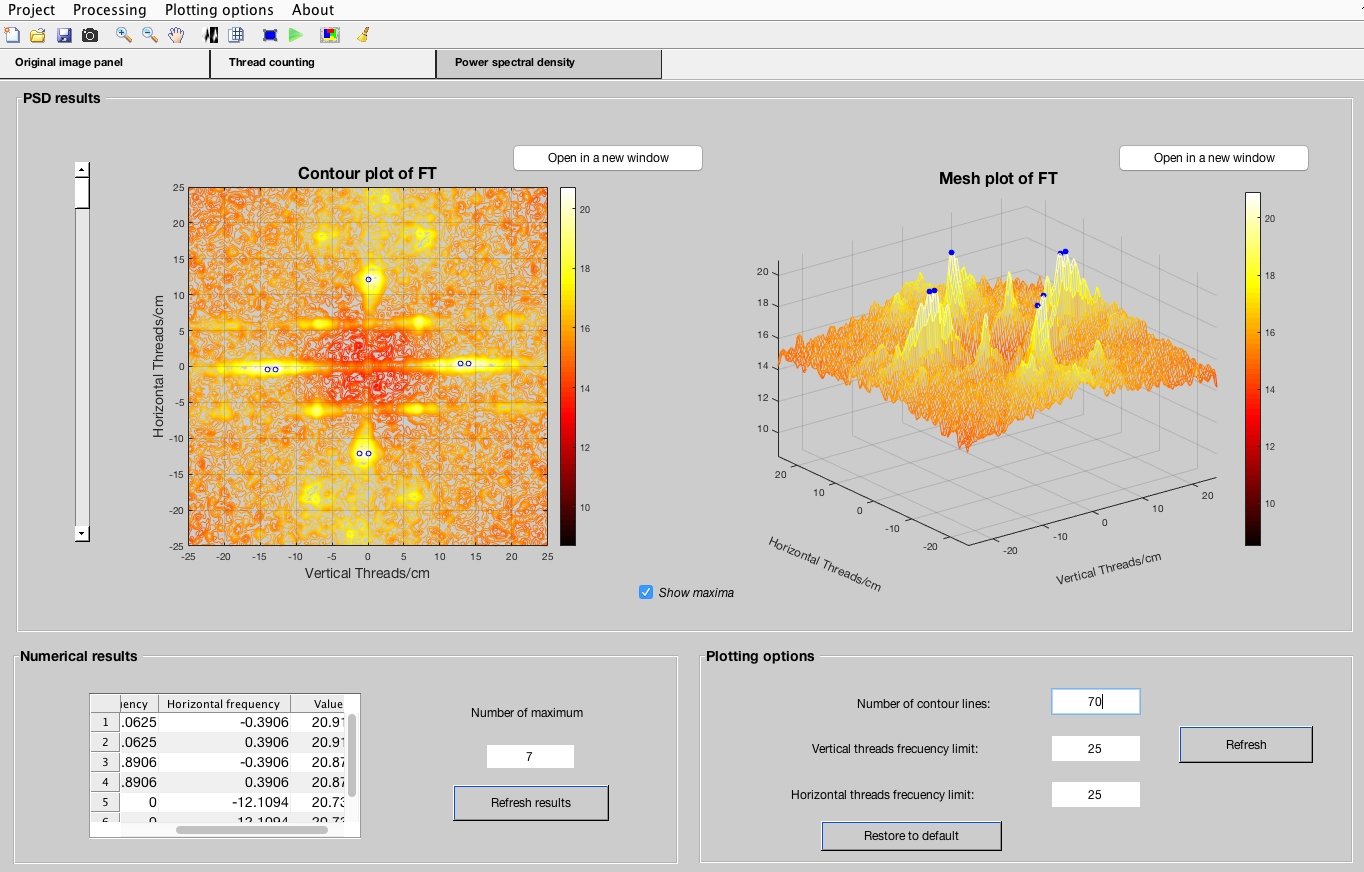
- In the ‘Power spectral density’ tab is possible to manipulate the frequency limits as well, and besides, the number of maxima showing in the plots Also, it is provided with a slide bar which shows the progress of the power spectral density calculation.
Note on parameters:
If you followed these simple steps above, the thread counting algorithm has been run with the parameters configuration set by default. Although these can be manipulated, it is recommended to consult the user’s manual beforehand in order to understand each parameter’s meaning and purpose.
Among the most interesting parameters you may find useful the first three ones: Resolution scaling, Shift and Size window.
