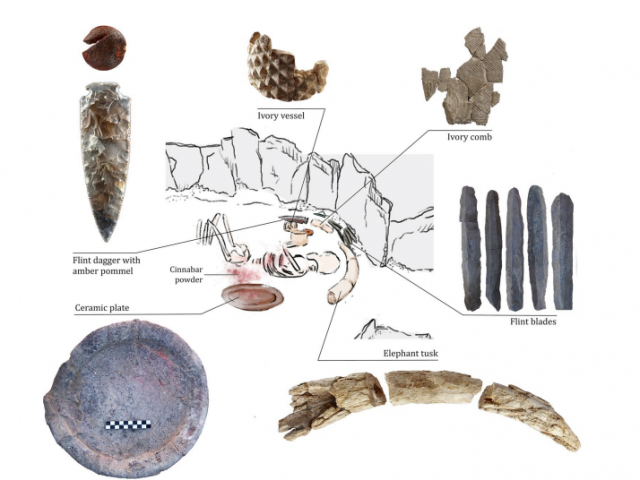
Given the absence of written records, the main source of information available to analyze gender inequalities in early complex societies is the human body itself. And yet, for decades, archaeologists have struggled with the sex estimation of poorly preserved human remains. Here we present an exceptional case study that shows how ground-breaking new scientifc methods may address this problem. Through the analysis of sexually dimorphic amelogenin peptides in tooth enamel, we establish that the most socially prominent person of the Iberian Copper Age (c. 3200–2200 BC) was not male, as previously thought, but female. The analysis of this woman, discovered in 2008 at Valencina, Spain, reveals that she was a leading social fgure at a time where no male attained a remotely comparable social position. Only other women buried a short time after in the Montelirio tholos, part of the same burial area, appear to have enjoyed a similarly high social position. Our results invite to reconsider established interpretations about the political role of women at the onset of early social complexity, and question traditionally held views of the past. Furthermore, this study anticipates the changes that newly developed scientifc methods may bring to prehistoric archaeology and the study of human social evolution.
Download: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-023-36368-x