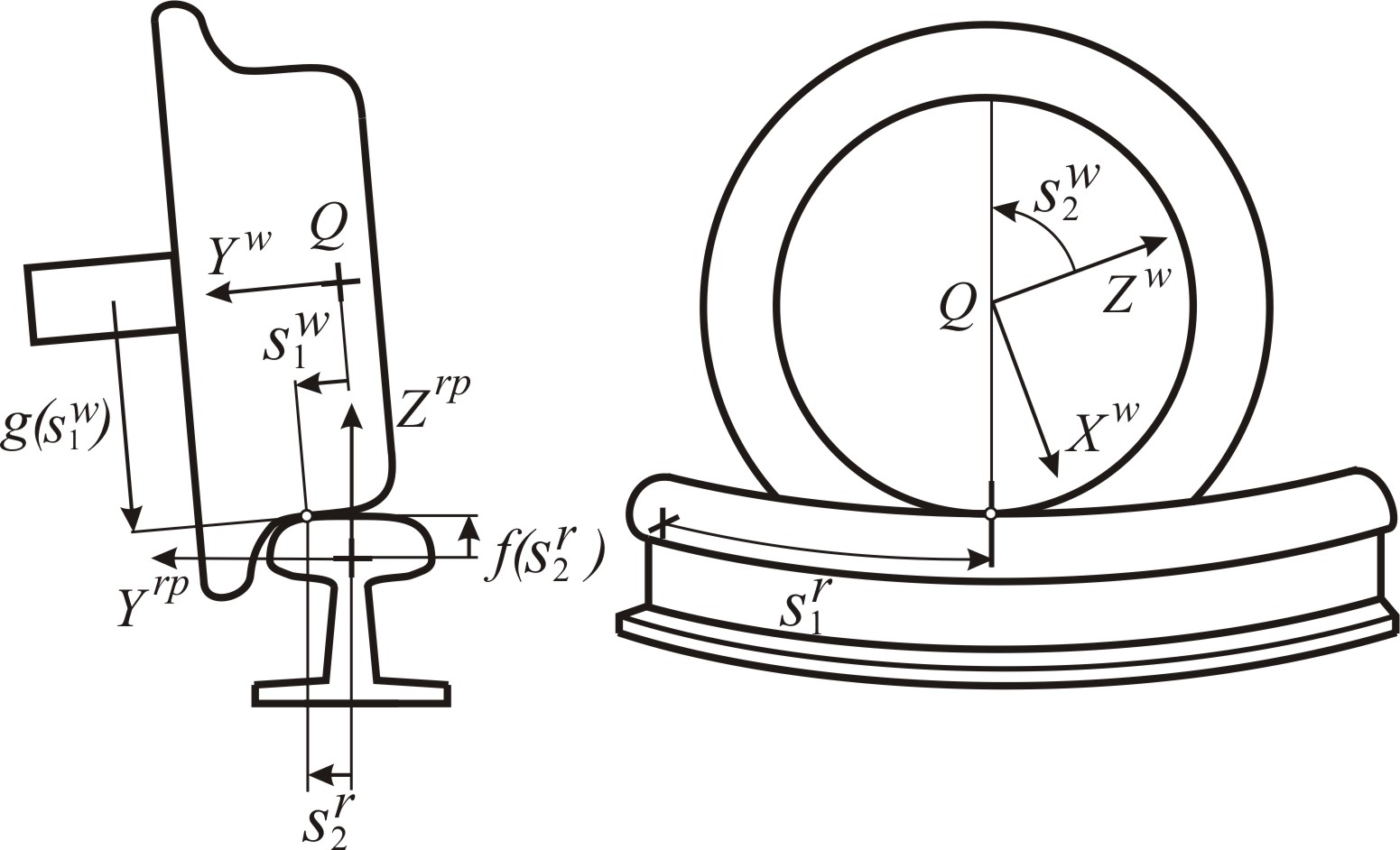
In multibody dynamic simulations of railway vehicles, the modelling of wheel–rail contact plays a fundamental role. Contact forces and their locations within wheel and rail profiles strongly influence in the dynamic behaviour of the vehicles. Two well-known approaches are commonly used to simulate wheel/rail contact in multibody railway simulations. The 1st is the elastic approach, in which interpenetration and separation between the wheel and rail surfaces is allowed and normal contact forces are computed, for example, using a Hertzian-based model that calculates normal contact forces using the interpenetration and interpenetration rate. The 2nd is the constraint approach, where the contact between wheel and rail is computed by solving a set of non-linear constraint equations that establish that both surfaces in contact coincide in one or more singular contact points without penetration or separation. In this approach, normal contact forces are described through the Lagrange multipliers, which are associated with the contact constraints at each contact point. One main feature of the elastic and the constraint approaches is the determination of the location of the contact points. In this sense, two methodologies can be used for this contact search. On the one hand, this search can be addressed using the online method. In this approach, the location of the contact points is determined at each time step of the dynamic simulation by solving a set of algebraic non-linear equations that evaluates the contact points as a function of the wheelset-track relative position. On the other hand, the search of the contact points can be done using the offline method.
Elastic aproach
Allows to model the contact and the separation of wheel and rail.
Lookup table method
Constraint method that searches for the contact points with an offline method.
KEC-method
Knife-edge Equivalent Contact constraint method.